Research progress on preparation of dissolving pulp for bio-based materials from straw in process engineering
 |
A long fiber; B short fiber
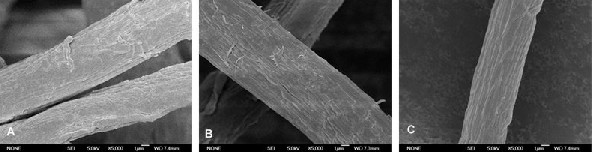
A Low-M dissolving pulp; B Dissolved pulp after cold alkali extraction; C High-A dissolving pulp after xylanase treatment
Dissolving pulp is a highly purified form of cellulose, used primarily as a raw material for producing cellulose derivatives such as viscose rayon, acetate fibers, cellophane, and carboxymethyl cellulose. It plays a vital role in the textile and chemical industries due to its high purity and consistent quality.
While various cellulosic sources can be used for dissolving pulp production, wood and cotton linters are traditionally the most common choices in industrial settings. However, agricultural crop straw has emerged as a promising alternative due to its abundance, low cost, and similar chemical composition to wood. Despite this potential, it has not been widely adopted in either domestic or international industries for dissolving pulp production.
Supported by key national research programs, including the "973" Plan (No. 2011CB707401), the "863" Plan (No. SS2012AA022502), and the National Key Science and Technology Support Project (No. 2011BAD22B02), the research team led by Professor Chen Hongzhang at the Engineering Research Institute made significant breakthroughs in using straw as a raw material for dissolving pulp. Their work challenged traditional methods and identified that the high content of heterocells in straw was a major barrier to efficient processing.
To overcome this, they proposed an innovative approach combining steam explosion with mechanical combing technology. This method enabled the effective separation of long and short fibers, significantly improving the quality of the long fibers. The long fibers obtained had a fiber cell content of up to 85%, comparable to that found in coniferous wood. Additionally, a new dry mechanical combing equipment was developed to support large-scale production.
After further refining the long fibers through cold alkali extraction and xylanase treatment, the resulting dissolving pulp achieved an α-cellulose content of 97.1% and a viscosity of 23.96 mPa·s—exceeding the standards for wood pulp used in viscose fiber production in China. This high-quality product meets the requirements for both low-mastic and high-mastic dissolving pulp applications.
The separated short fibers, which are more easily processed, can be efficiently converted into sugar for use in a variety of biorefinery applications. This integrated approach not only enhances the value of crop straw but also provides a sustainable solution for its utilization in industrial processes.
The findings of this research were published in the prestigious international journal Bioresource Technology (Bioresource Technology, 139 (2013): 59–65). This study represents a significant step forward in the development of eco-friendly and economically viable methods for converting agricultural waste into high-value products.
Floodlights,Outdoor Floodlight, Led Floodlight,Solar Floodlight
Jiangsu chuanglv Transportation Facilities Co., Ltd , https://www.clsolarlights.com